Psoriasis or scaly lichenIt is a chronic disease that affects the skin and its appendages: nails and hair. It is characterized by periods of deterioration (relapse) and temporary well-being, when the manifestations of the disease become less. This disease is not contagious and the patient is not dangerous to others. Because the occurrence of psoriasis is not associated with microorganisms.
Psoriasis most often occurs between the ages of 15 and 45. Light-skinned people are more susceptible to this. In developed countries, the number of psoriasis patients reaches 2-4% of the population. Every 25th inhabitant of the Earth on all continents suffers from it.
A huge number of medical institutions are dealing with this problem. Therefore, psoriasis is recognized as the most studied disease. However, this disease is not fully understood. It is officially considered incurable and raises many questions.
Psoriasis is caused by the body's own immune cells. They rise from the lower layers of the skin to the upper, causing inflammation, proliferation of epidermal cells and the formation of small capillaries.
The manifestations of psoriasis on the skin are quite diverse. Most often, the disease causes the appearance of red spots - psoriatic plaques. They are dry to the touch, rise above the surface of the skin and are covered with a white coating.
Types of psoriasis
The disease is divided into two major groups: pustular and non-pustular psoriasis.
Nonpustular psoriasis
- common (vulgar) or simple psoriasis (plaque psoriasis, chronic stable psoriasis)
- psoriatic erythroderma or erythrodermic psoriasis
Pustular psoriasis
- pustular psoriasis von Tsumbusch or generalized pustular psoriasis
- palmoplantar psoriasis (pustular psoriasis of the extremities, chronic persistent palmoplantar pustulosis)
- annular pustular psoriasis
- palmoplantar psoriasis
- herpetiformis psoriatic impetigo
In addition, these types of psoriasis are different.
- seborrheic psoriasis
- psoriasis of flexor surfaces and skin folds
- Napkin psoriasis
- drug-induced psoriasis
According to the severity, such forms of psoriasis differ.
- Mild - less than 3% of the skin is affected.
- Moderate - 3-10% of the skin is covered with psoriatic plaques.
- Severe - there are lesions of the joints or more than 10% of the skin is affected.
Causes of psoriasis

To date, there is no unequivocal answer to the question: "Why does psoriasis occur? " Scientists have put forward several theories.
- Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease. It is based on a malfunction of the immune system. Immune cells of T-killers and T-helpers, whose function is to protect the organism from viruses, bacteria and tumor cells, for some reason penetrate the upper layers of the skin. Here they produce inflammatory mediators - substances that "trigger" the inflammatory response. The result is increased division of skin cells and their proliferation (proliferation).
- Psoriasis is a disease caused by impaired growth, division and maturation of epithelial cells - keratinocytes. The result of such changes in the skin is an attack of immune cells T-lymphocytes and macrophages on diseased skin cells.
Factors that contribute to the development of psoriasis
Doctors have identified a number of factors that can cause the disease. Of course, psoriasis most often occurs if several of these conditions affect the body at once.
- Hereditary predisposition.There is a version that the genes responsible for the immune system and T-lymphocyte function are carriers of the disease. Therefore, parents who suffer from psoriasis are more likely to have children who have the same symptoms.
- Thin dry skin. . . It has been observed that people with such skin characteristics are more likely to get sick than those with oily and well-hydrated skin. This is probably due to the protective functions of sebum and the structural characteristics of the skin.
- External irritants. . . A high percentage of patients are among those who are in constant contact with alcoholic solutions, solvents, household chemicals, cosmetics (lotions, hand creams).
- Excessive hygiene- Excessive love of cleanliness also undermines the protective properties of the skin. Soaps, shower gels and washcloths wash away the natural protective barrier and leave behind microscopic injuries.
- Bad habits- Addiction to alcohol, smoking and drugs is bad for the skin. Her diet and blood supply are deteriorating.
- HIV- AIDS patients are more prone to psoriasis. Scientists cannot explain this phenomenon. The fact is that psoriasis is caused by increased activity of lymphocytes, and in AIDS their number decreases.
- Medications- taking certain medications can cause illness. Among them: beta-blockers, antidepressants, anticonvulsants and anti-malarial drugs, lithium carbonate.
- Infections (fungi and staphylococci). . . It is not uncommon for psoriasis to appear immediately after fungal infections or diseases caused by streptococcus.
- Movement- Climate change or even the seasons, environmental degradation can be a trigger for this disease.
- Stress- severe emotional disturbance or physical stress (long periods of hypothermia, overheating, accidents) precede the appearance of the first symptoms of psoriasis.
- Trauma- permanent effect on the skin: pressure, friction, scratching. Such regular trauma can cause the first psoriatic plaques to appear at this site.
- Allergic conditions- Allergic skin rash and the processes that occur in all layers of the skin in this case also increase the risk of disease.
What are the symptoms and signs of psoriasis?
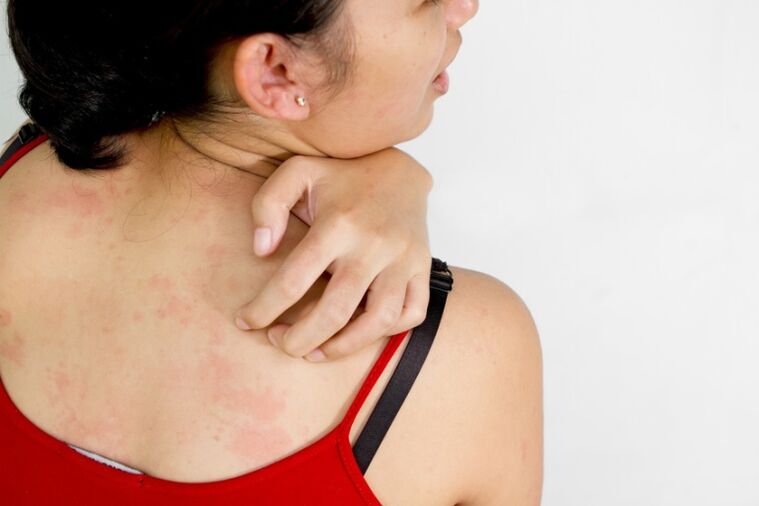
Psoriasis is a systemic disease that affects more than the skin and nails. It affects the joints, tendons and spine, immune, nervous and endocrine systems.
But still, the main manifestations of the disease occur on the skin. The name squamous lichen quite accurately conveys the symptoms of psoriasis. The first manifestations are often pink or bright red papules of regular rounded shape, covered with scales - psoriatic plaques. They are located symmetrically, mainly on the extensor surfaces, lower back and scalp. But they can affect any part of the skin and mucous membranes of the genitals. Their size is from a few millimeters, in the initial stages, to ten centimeters or more.
Depending on the characteristics of the rash, e. g.forms of psoriasis:
- Pitting psoriasis - the size of the elements is smaller than the head of the needle.
- Guttate psoriasis - the papules are teardrop-shaped and reach the size of a lens.
- Cochlear psoriasis - plaques grow up to 3-5 mm and have rounded edges.
They also distinguish the forms of rash, when its elements are in the form of rings, arches and wreaths, geographical maps with jagged edges.
The papules are covered with a scaly coating that can be easily removed. It consists of keratinized epidermal cells. Psoriatic plaques begin to cover with scales from the middle, and then the plaque spreads towards the edges. Its loose and light appearance is due to the fact that keratinized cells are permeated with spaces filled with air. A pink ring can form around the elements - this is the area of inflammation, the zone of plaque growth. The skin around the elements of the rash has not changed.
Scalp psoriasisrepresents psoriatic plaques that rise significantly above the surrounding skin. They are densely covered with dandruff-like scales. In this case, the hair remains unchanged. The rash can appear not only under the hair, but also on smooth skin, on the neck and behind the ears. Such changes are explained by the active division of keratinocytes in the affected areas.
Psoriasis of the feet and palmscauses a strong thickening of the stratum corneum on these parts of the body. The skin becomes thick, rough. Cracks often penetrate it. This is caused by intense cell division, which multiplies 8 times faster than usual, but is not removed in time from the skin surface.
Nail psoriasisit differs in various symptoms. But the two most important are the two main types of nail plate damage:
- By type of "thimble". Small holes are formed on the nail plate, similar to the traces of a needle prick.
- By type of onychomycosis. The lesions resemble nail fungus. Nails thicken, change color, peel. A psoriatic papule surrounded by a red border is visible through the nail plate. It looks like a stain of oil shining through the nail.
The symptoms and signs of psoriasis depend on the stage of the disease, which changes cyclically throughout the year. Thus, most patients have a "winter" type of disease, when the worsening occurs in the autumn-winter period. The improvement in summer is due to the fact that ultraviolet light in the sun has a therapeutic effect. But some patients suffer from the "summer" type.
There are the following stages of the course of psoriasis:
- progressive - the appearance of new elements, the active growth of existing plaques, the implicitness of the pink growth zone around them, intense peeling and itching.
- stationary - stopping the growth of papules, the absence of new rashes, fine folding of the upper layer of skin around psoriatic plaques.
- regression - the absence of peeling, the disappearance of plaques and the appearance in their place areas of pigmentation, indicate a weakening of the process.
What does a skin rash with psoriasis look like?
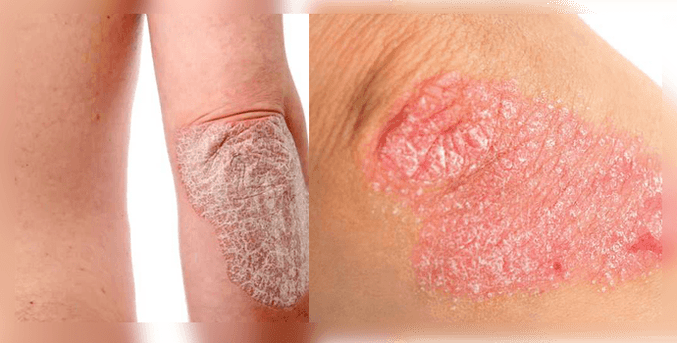
Each organism is individual and reacts differently to the disease. Therefore, the nature of the rash can be very diverse. This explains the variety of forms and types of psoriasis.
However, for most people, the symptoms of psoriasis are similar. These are red spots - psoriatic plaques, which rise 1-3 mm above the level of healthy skin. Their appearance is caused by the fact that the cells of the surface layer of the skin - keratinocytes, divide very actively, do not have time to mature and turn into full-fledged epithelial cells. As a result of this increased pathological growth, certain areas of the skin thicken. This is due to the fact that immune cells release chemicals that cause skin inflammation.
From above, the plaques can be covered with a gray, silver or yellowish inflorescence, which looks like paraffin. That is why they got the name - "paraffin lakes". These are keratinized epithelial cells whose rejection is disturbed and accumulates on the surface of the affected skin.
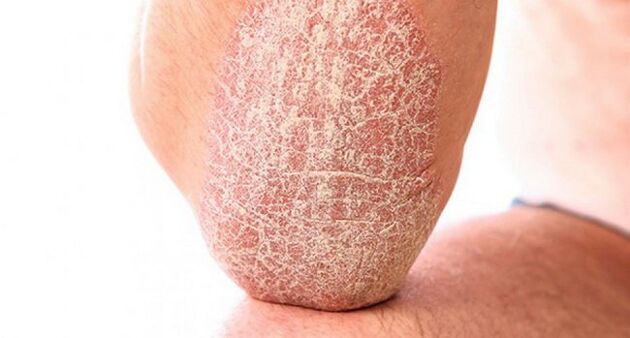
Freckles are scaly, warmer than the rest of the skin and can grow to a large size. Often the patient feels severe itching at this site. This is due to the fact that a cascade of neuro-reflex reactions and an allergic reaction occur on the background of the inflammatory process.
The other type of element is papules. These are small elements of the rash that resemble tuberculosis. The size is about 1 mm. There is no cavity filled with contents in the middle. They are often found on the knee and elbow joints. They remain even in periods when the disease recedes.
During exacerbations, the elements of the rash gradually grow in width and merge with the adjacent plaques. During the period of improvement (remission), the spots begin to shine from the middle. They gradually take the shape of a ring and can be completely dissolved. After plaques on the body remains a trace - pigmentation. It can be significantly lighter or darker than the surrounding skin. After a person has tanned, the skin tone is usually even.
What do nail lesions in psoriasis look like?
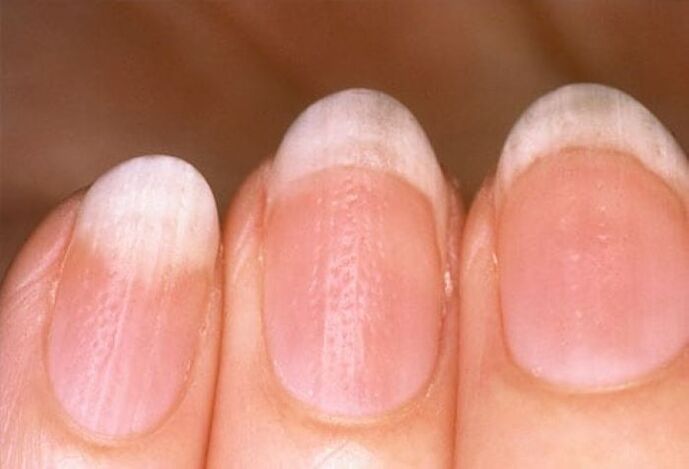
Nail psoriasis is similar to a fungal infection of the nail plate. For a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to perform a laboratory analysis. The changes can affect just one nail or all at once and are very diverse. They occur in 10-15% of patients. Nail damage is often accompanied by joint pain caused by psoriasis. In this case, there may be no rash on the skin.
Nail psoriasis has several stages:
- depressive points - fingernail
- longitudinal concave grooves
- transverse compression in the center of the nail, these first signs are associated with damage to the root of the nail - the nail matrix
- "Oil stains" pink spots of irregular shape that are visible through the nail - it is the accumulation of serous fluid under the nail
- the nail becomes dull, blurred, yellow and thickened due to circulatory disorders
- the nail plate takes on the appearance of a bird's claw, which is accompanied by pain. This is due to the fact that the process catches the nerve endings.
The nail lesions start from the edge and gradually move towards the root, covering the entire surface. Disorders of microcirculation cause blurring of the nail and change of its color from yellow to bluish.
If you find similar symptoms in yourself, do not diagnose yourself. Similar changes can be caused by other reasons: fungus, trauma, and impaired blood supply.
Is psoriasis contagious?
This question is often asked by those who have just been diagnosed with the disease and acquaintances of the patient. Scientists give an unequivocal answer to that. Psoriasis is not contagious, and a sick person is absolutely safe for others. This is because psoriasis is not caused by viruses or bacteria, but by aggressive white blood cells. These own immune cells, for unknown reasons, attack skin cells, causing inflammation of the skin. The result of this process is a rash and thickening of the skin in some places (psoriatic plaques).
How is psoriasis treated?
The treatment of psoriasis depends on the form and stage of the disease and the sensitivity to the drugs. Traditional medicine focuses on the use of medicines. Treatment begins with topical preparations that act on the affected skin. Therefore, they try to avoid the side effects that occur when taking oral medications. More details on the use of topical medications will be described below. Now let's stick to pills and capsules.
There is a technique when the patient is first offered milder medications with the least number of side effects. If they are not effective, they are replaced by stronger ones and so on. Even if the treatment is suitable for the patient, it changes after a while. The fact is that the body gradually gets used to the drug and its effect is reduced.
Oral systemic drugs are very effective. They are prescribed for moderate and severe stages of the disease. They help even those patients in whom treatment with other means did not give a positive result. However, they have significant disadvantages: they can cause serious side effects, and after the abolition of these funds, the condition worsens again.
| A group of drugs | Dosage form and effect of the drug on the body |
| Retinoids - derivatives of vitamin A. | It affects the maturation of the surface layer of the skin and eliminates disturbances in this process caused by psoriasis. Release form - capsules. Dosage according to the scheme, depending on the phase, 30-75 mg / day. It reduces the rate of keratinocyte division, promotes normal cell maturation and differentiation. Available in capsules. The daily dose is 25-50 mg. |
| Immunosuppressants - drugs that reduce the activity of the immune system | It reduces the activity of T-lymphocytes, which cause increased division of skin cells. Sterile solution in ampoules. The initial dose when given intravenously is 3-5 mg / kg per day, for oral administration - 10-15 mg / kg per day. |
| Drugs for the treatment of malignant neoplasms (cytostatics) | Inhibits excess growth and reproduction of atypical epidermal cells. Available in tablets. Assign 2, 5-5, 0 mg orally, 2-3 times a day, 1 time a week. |
Physiotherapy treatments for psoriasis are very effective. They bring significant relief to patients, stop the progression of the disease and, in some cases, serve as a safe substitute for medication.
| Physiotherapy method | Effects on the organism |
| PUVA therapy or photochemotherapy | A combination of long-wave ultraviolet radiation and an internal photosensitizer. The course is 20-30 procedures. The method is based on the fact that UV rays penetrate deep into the skin. The photosensitizer inhibits the synthesis of skin DNA cells and the rate of their division. Special installations or cabins are used for treatment. |
| Selective phototherapy (S. F. T. ) | Irradiation of the skin with ultraviolet rays of wavelength 280-320 nm. The course is 15-35 procedures. A special cabin is required for therapy. |
| Monochromatic UV treatment | Exposure to each focus separately with a laser or UV lamp. It allows you to irradiate hot spots even in hard-to-reach places, without affecting healthy skin. It is prescribed in cases when less than 10% of the skin is affected. The course of treatment is 15-30 procedures. |
| Laser therapy | Laser radiation of different wavelengths is used to treat rashes. The laser promotes rapid resorption of psoriatic plaques, protects against the appearance of scars in their place. The doctor determines the number of procedures individually for each patient. |
| Electrosleep | The procedure is performed on a device based on a mild effect on the brain with weak electrical impulses. Duration 20-60 minutes. The number of procedures is 10-12. Electrosan has a calming effect. As a result, the activity of the nervous system is normalized, the plaques begin to dissolve, and the period of well-being begins faster. |
| Magnetotherapy | Magnetic field treatment has a beneficial effect on the general condition. It reduces itching and inflammation of the skin, swelling and pain in the joints, improves the psycho-emotional state. The Betatron device is used for treatment. The duration of the procedure is 20 minutes. Number per course 10-15. |
| Ultrasound therapy | It is used as a painkiller, antipruritic and decongestant. Promotes scar resorption. The procedure can be combined with the use of drugs (phonophoresis). The duration of exposure in one area is 15 minutes. It takes 7-14 sessions to achieve a therapeutic effect. |
| Hyperthermia | Heating fabrics to a temperature of 40 degrees using special pillows with a thermal mixture. This effect on the body normalizes the work of the immune system, and reduces the attack on the skin. The duration of the procedure is about 2 hours. Their number is determined by the doctor. |
| Bee venom treatment | The substance is introduced into the body by electrophoresis or ultrasound. An anti-inflammatory, absorbent, antipruritic effect is achieved. Metabolism is normalized. The minimum number of procedures is 10. |
It is very important for people with scaly lichens to adhere to a diet. Eating disorders can make the disease worse. The menu should be rich in vitamins and simple at the same time. It should rest the intestines and liver, and also not cause allergies to the body.
| Allowed products | Forbidden food |
| Vegetables (pumpkin, watermelon, beets, carrots, potatoes, radishes) | Animal fats |
| Fruits (apricots, peaches, apples), juices | Alcohol |
| Berries (except red berries: strawberries, raspberries, red currants) | Fatty meat (pork, duck) |
| Fresh herbs | Smoked meat |
| Lean meat (veal, beef, rabbit, turkey) no more than 200 g per day | Red fish |
| Cheese, cottage cheese, dairy products | Carbonated drinks and coffee |
| Nuts | Eggs |
| Low-fat varieties of fish | Ice cream and milkshake |
| Seaweed | Minimum amount of confectionery and sugar |
| Whole grain bread | Butter and puff pastry |
To cleanse the body of toxins and metabolic products, it is necessary to fast twice a week. They recommend kefir, apples, vegetables.
Which ointments are effective in treating psoriasis?
The use of ointments for psoriasis brings the greatest effect compared to other external preparations. The components of the fat do not remain on the surface of the plaque, but soften the scales and enter the skin.
There are a number of ointments available to treat psoriasis. In the early stages to appointnon-hormonal fats.
If the treatment did not give the expected effect, then prescribehormonal fats. . . Treatment begins with lighter medications that have minimal side effects. If improvement is not achieved, then stronger fats with glucocorticosteroids are prescribed.
| The name of the fat | Drug action | Side effects |
| Low fat | Suppresses increased activity of leukocytes, prevents their movement into the skin, eliminates the feeling of tightness and itching. | Swelling of the skin, itching, redness. |
| Moderate fats | It has anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, antiedematous, antipruritic action. Suitable for patients with exudative forms of psoriasis, reduces bleeding. Apply in a thin layer on limited areas 2-3 times a day. The treatment lasts 10-14 days. | Steroid acne, atrophy and stretching of the skin, tingling, itching, hypopigmentation. |
| Strong fats | Topical anti-inflammatory, antipruritic and antiallergic agent. Reduces skin moisture. Apply to the affected area 2-3 times a day for up to two weeks. It is used during exacerbations. | Skin atrophy. |
| Very strong fats | It has a strong antipruritic and antiallergic effect. It slows down the processes of cell division and keratinization. Apply 1-2 times a day for no more than two weeks per course. | Acne, hair loss, skin atrophy. Do not use for pustular and widespread plaque psoriasis. |
Pharmaceutical companies produce many drugs in the form of ointments. The doctor individually selects the drug for the patient and, if necessary, changes it to a stronger one.
Remember that in any case of psoriasis, you should not neglect a visit to the doctor. After all, this disease can hide the initial stage of skin cancer.
Choosing a psoriasis treatment regimen is a time consuming process that involves many trial and error. Don’t despair if you don’t find "your" cure right away. Remember that many people achieve lasting improvement when the disease does not return for years. And you can do it!























